Related: Understanding Kubernetes Resources for K8s concepts, Kubernetes + Docker for container basics, Best Practice Production for production patterns, Monitoring for homelab monitoring
Build a Homelab with Talos OS and Proxmox
Preface
So i recently have an idea to deploy my project on the cloud using Kubernetes, i went on browsing to several cloud providers and found that they charge around $0.1 per hour, for the lowest tier support
- Google Cost about $101 == ¥15000 per month for the specification 0.25vCPU and 1GiB of RAM
- Amazon Cost about $70 == ¥10350 per month for the same specification
When i was browsing amazon, i found that amazon sold a very decent mini pc for a cheap price BMax Mini PC Turbo
- DDR4 16 GB
- 512 GB SSD
- 4 Core
If we see the Google Cloud with the same spec it cost around $280 == ¥41500 per month. That’s a lot of money :“DD, so based on this findings i decided to build my on homelab. To do this
but when i go to was thinking why i don’t build my own server and expose it to internet? I so this is it. In this blog i will covers how can you do it too by yourself using an unused/new computers to build your own server.
Table Of Content
What you need
- Machine Unused Computer/Mini PC
- Internet Connection
- Router/Switch [Optional]
- LAN [Optional] this method is prefered since it’s easy to do most of the machine have eth0/lan interface
- If your machine have wireless network card interface then it should be ok
- USB Flashdisk 4GB or More

Goal
We want to setup a Kubernetes cluster in our home machine, and to verify the cluster we will deploy an Nginx pod inside this cluster. The first step is to choose which flavor of Kubernetes we want to use
We can categorize Kuberentes flavor into two, for development and production ready
For Development
In this category we can use kubernetes that very easy to setup. This flavor is suitable for development purpose only. We don’t consider this for production since it’s only run on a single node (even though we can create multi-node for Kind) and also not suitable for high availability.
Most of them run docker container as the node of the kubernetes cluster. So you need to have docker installed in your machine first before using this flavor. I have use all of them and i found that kind is very good since you can create multi-node cluster easily with yaml configuration. There are many more kubernetes flavor for development purpose, but i think these are the most popular one.
Production Ready
This kubernetes flavor is suitable for production since it can run on multiple nodes and also support high availability. Some of the flavor are:
Actually there are many more flavor than i listed above but i have personally tried K3s, Talos, and MicroK8s.
| Comparison | Talos | K3s | MicroK8s |
|---|---|---|---|
| Size | Very Small | Moderate | Quite Big |
| Type | Bare-metal OS | Binary | Snap |
| Installation | Quite Complex | Simple | Simple |
| Features | Minimal | Moderate | Rich |
NOTE
Why i say talos is minimal is because by if we compare the default installation of talos with k3s and microk8s, talos only have the basic features that are needed to run kubernetes. While k3s and microk8s have a lot of features such as storage, ingress, dashboard, etc. that are installed by default.
This Video explain different flavor of kuberentes, pros and cons.
And i found that Talos is the most interesting one since it’s a bare-metal os. What is that means? If we look at k3s or microk8s. They are installing kubrenetes nodes inside of the OS (like ubuntu, debian, etc). While talos is an operating system by itself. So i was curious about this and chose this in this blog. So in this blog we will use Talos as our kubernetes flavor.
Plan
Since we will be using Talos OS as our kubernetes flavor, we will be installing Talos to our machine. We can install Talos directly to the machine but i want to have more flexibility in managing my virtual machine. So i will be using Proxmox OS as my hypervisor. Proxmox is a free and open source KVM hypervisor that can be used to create and manage virtual machines.
What makes proxmox interesting is that it have a web interface that can be used to manage the virtual machines. So we can create, delete, and manage the virtual machines easily using the web interface.
NOTE
Why we don’t use windows and use virtualbox or vmware workstation? actually you can, but maybe it will be more limited and hard since the virtualization is not on the kernel level. Besides that i want to have a more production like environment so i want to learn how to use proxmox since it’s a popular hypervisor in the industry.
- Install Proxmox OS to our machine
- Install Talos OS inside Proxmox VM
- Configure Kubernetes Cluster
- Deploy Nginx Pod to verify the kubernetes cluster
Setup Proxmox
- Download Proxmox ISO from here i use the latest version
Proxmox VE 9.0 - Prepare a USB Stick with at least 4GB capacity
- Burn the ISO to the USB Stick using Rufus for Windows or balenaEtcher for MacOS. I haven’t tried to use linux computer to burn the ISO, so you can try it by yourself. Official Guide from Proxmox
- After the Burning process is complete, plug the USB Stick to the machine that you want to install Proxmox
- Restart the machine and enter the BIOS/UEFI settings, for this BMax Mini PC Turbo you can spam delete button after restarting the machine
NOTE
Different hardware have different way to enter the BIOS/UEFI settings, you can search it on google by searching
how to enter bios/uefi settings on <your hardware>
- Change the boot order to boot from USB Stick first to install it
- In the first prompt, you will be asked to input username, password and email.
- After this you will be prompted to input FQDN, IP Address, Gateway, and DNS Server, See the Proxmox - Network section for more detail
- After this you can hit next next and let the installer boot the Proxmox OS
After the installation is complete, you will be prompted by a login form. Proxmox by default will provide UI Interface at the http://IP:8006.
NOTE
The default
usernameisroot. The password is the one you put on the installation previously

Proxmox - Network
- Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN)
- This is a hostname that proxmox had. You can input anything as long this is FQDN
- For me i input
citadel.gawrgare.home - IP Address / CIDR
- Gateway
- DNS Server
- Gateway is how can router connect to external internet. This IP is usually ends with
1. For example192.168.0.1 - IP Address / CIDR is the range of IP Address that will be used by Proxmox
- Note that you need to reserve some IP from your router to make sure that these range of IP Addresses is not being used by your router
DHCP - If you’re not sure, you
- Note that you need to reserve some IP from your router to make sure that these range of IP Addresses is not being used by your router
- DNS Server
NOTE
DHCP Server is a mechanism that used by router to assign an IP to a device. It uses a lease mechanism to give machine and IP from the available list
MacOS
- Go to setting, and find
WiFi Setting - You can find the IP Address and Router here.
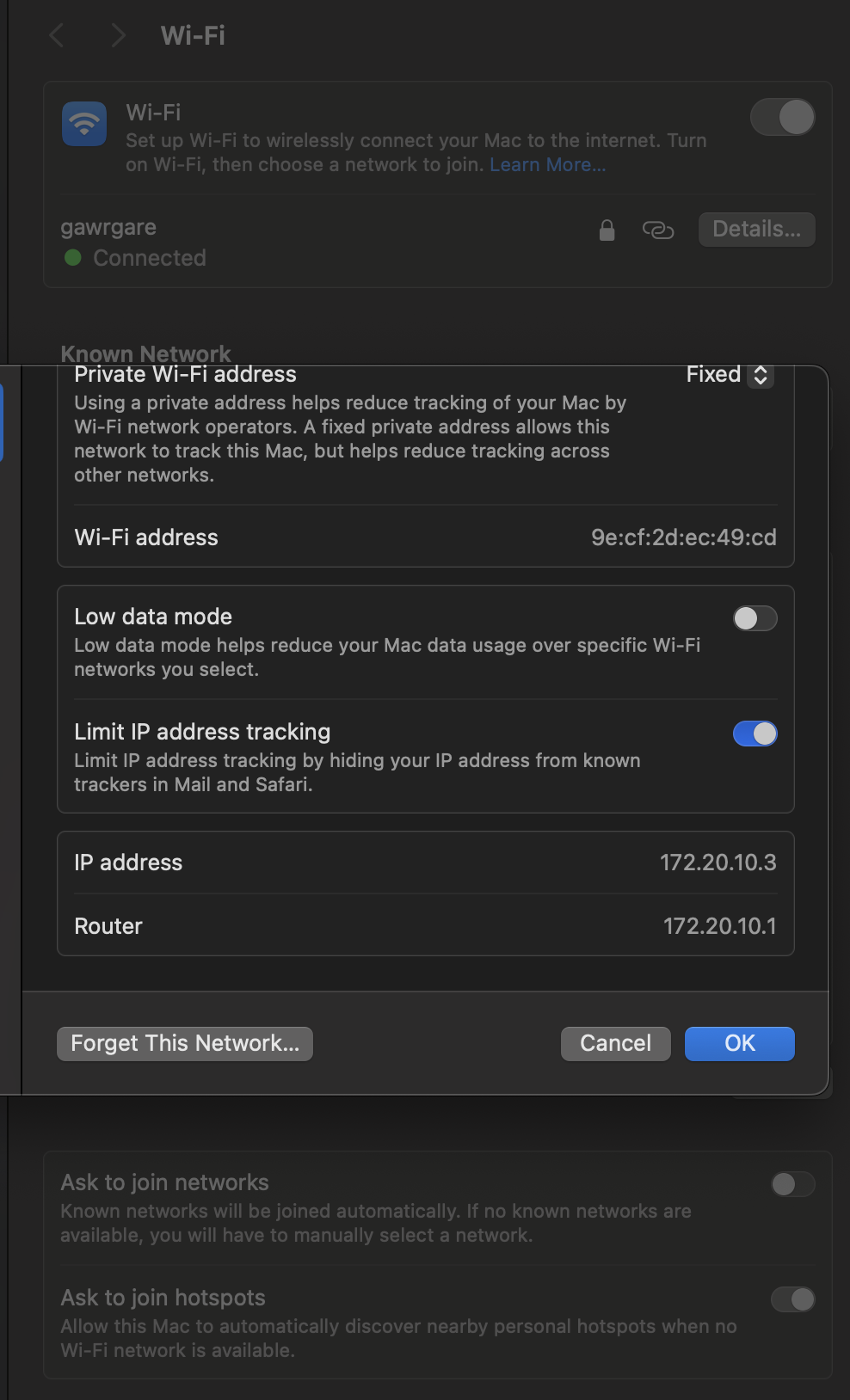 Or you can enter
Or you can enter ifconfig in terminal, it will output the same result
Windows
- For windows you can use
ipconfig -a
TIP
You can visit No IP Websitefor the detail on how to get your IP You can find more detail about proxmox in their official Proxmox Installation Guide and also this video explaining about installing proxmox step by step
Setup Talos
After Proxmox Installation is completed, now we need to install Talos inside of the Proxmox.
There are two ways to setup virtual machine in Proxmox, Manual via UI and [Terraform][#]. In this guide i will show you both ways. My personal preference is to use terraform since it’s more reproducible and easy to manage. But if you are new to terraform then you can use the manual via UI method.
Manual via UI
To install manually, we can start by login the web interface that Proxmox has given. And download the OS
- Talos is Very Nice and give us an options to chose via Image Factory
- If you’re not sure just pick the default image
- Pick the right architecture for your machine, for me i will use
amd64 - Talos provide a lot of extensions that you can use, you can pick the one that you need. For me i will pick
siderolabs/gvisor,siderolabs/iscsi-tools, andsiderolabs/util-linux-tools. - If you’re using older Talos version you need to add
net.ifnames=0to the extra kernel args to make sure that the network interface is namedeth0instead ofens18or something else - After all complete, it will show you lot of a link and a hash of your choice. For example
efb7577422715f84c716c3d30fee60858fb093841d1d539ca5db92ae99737bf8. The URL of download essentialy isfactory.talos.dev/metal-installer/[hash_id]:[version]. So based on the schematic id it will befactory.talos.dev/metal-installer/efb7577422715f84c716c3d30fee60858fb093841d1d539ca5db92ae99737bf8:v1.11.1. - Click the local-lvm and copy the ISO link generated by talos factory
- Go to Proxmox web interface, and create a new VM
- Pick any name that you want, we will create 2 VM 1 for control-plane and worker so i will name
talos-control-planeandtalos-worker1 - In the OS section, choose the ISO that you have downloaded previously
- In the System section you can leave it as default
- In the Hard Disk section you can allocate 20GB or more for the disk size
- In the CPU section make sure the type is
x86-64-v2-AESand you can allocate 2 core or more, i will chose 2 core - For Memory you can allocate 2048MB or more, i will chose 4096MB
- In the Network section leave it as default and click finish
TIP
- Since talos is very minimal, Storage system in kubernetes is not included by default. So if you want to use storage in your kubernetes cluster you need to install
siderolabs/util-linux-toolsandsiderolabs/iscsi-toolsextension- If you want to have Static ip for the OS, you need to choose the
Cloud Serverand pickNoCloud. In this guide i choose the bare-metal since it is the simplest one- You can directly click this link to download the same image as mine
- You can see the detail guide in Talos Official Documentation
Wait until it’s finish booting and you should see this, the status should be Maintenance.
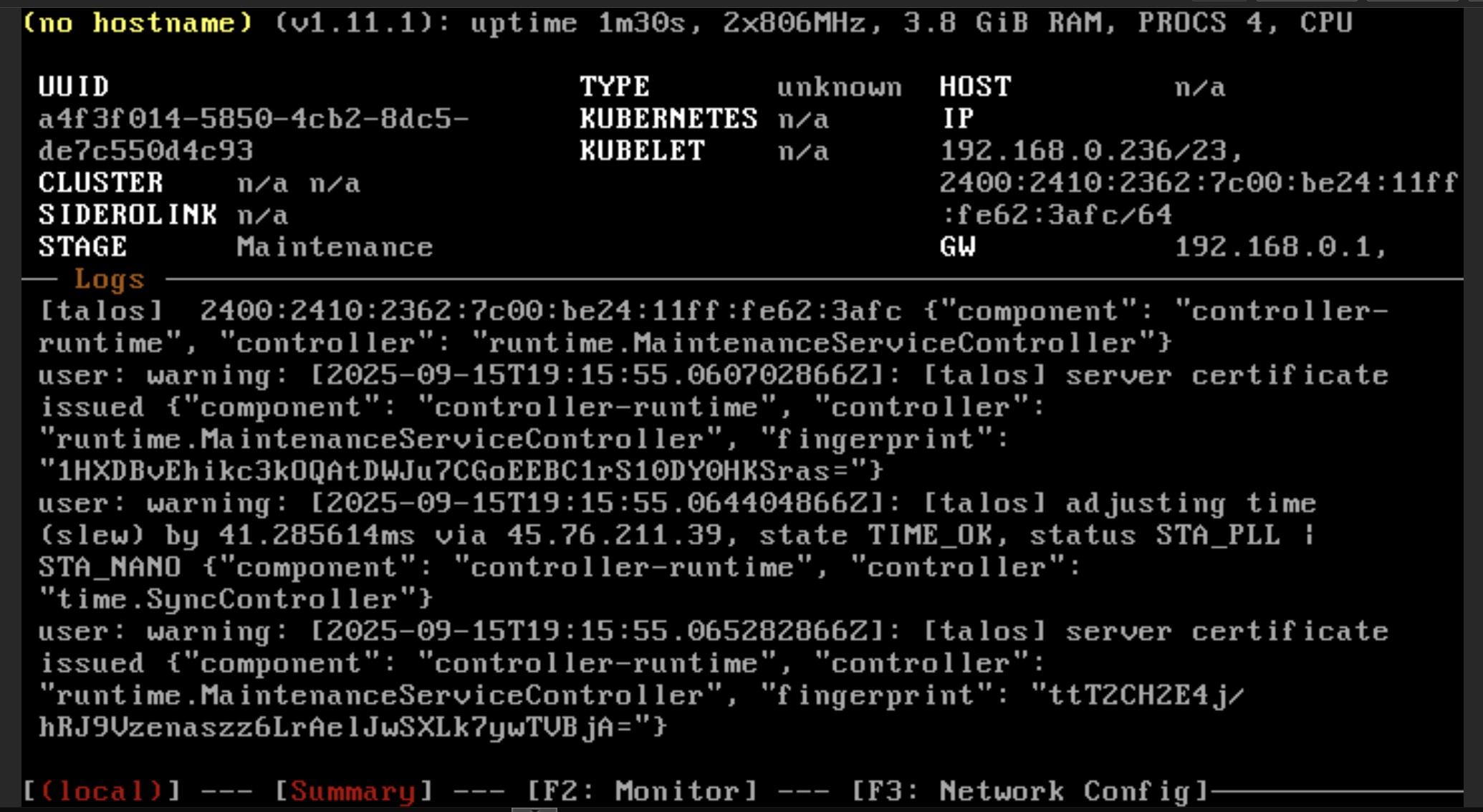
WARNING
You need to this step twice, 1 for control-plane and 1 for worker
Installing via Terraform
I want to use terraform to manage my Proxmox. This section is completely optional you can skip it and straight to configuring Talos. To use terraform in Proxmox, we need to create a user in proxmox that has specific role attached to it. After the user has been created we will create a token specific for that user and will use it in the terraform.
Proxmox Terraform User Setup
We need to go to shell in the root of our proxmox datacenter.
- Create User for terraform in proxmox
pveum user add terraform@pve- Create role for the users
pveum role add Terraform -privs "Realm.AllocateUser, VM.PowerMgmt, VM.GuestAgent.Unrestricted, Sys.Console, Sys.Audit, Sys.AccessNetwork, VM.Config.Cloudinit, VM.Replicate, Pool.Allocate, SDN.Audit, Realm.Allocate, SDN.Use, Mapping.Modify, VM.Config.Memory, VM.GuestAgent.FileSystemMgmt, VM.Allocate, SDN.Allocate, VM.Console, VM.Clone, VM.Backup, Datastore.AllocateTemplate, VM.Snapshot, VM.Config.Network, Sys.Incoming, Sys.Modify, VM.Snapshot.Rollback, VM.Config.Disk, Datastore.Allocate, VM.Config.CPU, VM.Config.CDROM, Group.Allocate, Datastore.Audit, VM.Migrate, VM.GuestAgent.FileWrite, Mapping.Use, Datastore.AllocateSpace, Sys.Syslog, VM.Config.Options, Pool.Audit, User.Modify, VM.Config.HWType, VM.Audit, Sys.PowerMgmt, VM.GuestAgent.Audit, Mapping.Audit, VM.GuestAgent.FileRead, Permissions.Modify"- Create role
pveum aclmod / -user terraform@pve -role Terraform- Get the token
pveum user token add terraform@pve provider --privsep=0You will get something like this. Copy the value of the token and save it somewhere
│ key │ value │
╞══════════════╪══════════════════════════════════════╡
│ full-tokenid │ terraform@pve!provider │
├──────────────┼──────────────────────────────────────┤
│ info │ {"privsep":"0"} │
├──────────────┼──────────────────────────────────────┤
│ value │ xxxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx |
terraform@pve!provider=xxxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxxTerraform Files
- Create an empty directory and add the Proxmox providers, we will called this file
versions.tf
terraform {
required_providers {
proxmox = {
source = "bpg/proxmox"
version = "0.83.0"
}
}
}
- After that install the providers using
terraform init -upgradeto install providers in local directory - Add configurations for the Proxmox providers in file called
providers.tf
provider "proxmox" {
endpoint = var.proxmox_endpoint
api_token = var.proxmox_api_token
insecure = true
ssh {
agent = false
username = var.proxmox_username
password = var.proxmox_password
}
}- Add a file called
variables.tf, this file will be kind of our.envfile for this configurations
variable "proxmox_endpoint" {
type = string
description = "The endpoint for the Proxmox Virtual Environment API (example: https://host:port)"
sensitive = true
}
variable "proxmox_api_token" {
type = string
description = "The token for the Proxmox Virtual Environment API"
sensitive = true
}
variable "proxmox_username" {
type = string
description = "The username for the Proxmox Virtual Environment API"
sensitive = true
}
variable "proxmox_password" {
type = string
description = "The password for the Proxmox Virtual Environment API"
sensitive = true
}
variable "proxmox_node_name" {
type = string
description = "The node name for the Proxmox Virtual Environment API"
default = "pve"
}
variable "proxmox_datastore_id" {
type = string
description = "Datastore for VM disks"
default = "local-lvm"
}- Create a file called
.auto.tfvarsto fill our variables configurations, this is my example of the configurations
proxmox_endpoint = "https://192.168.1.2:8006/"
proxmox_api_token = "terraform@pve!provider=3f2c9ecb-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx"
proxmox_node_name = "citadel"
proxmox_username = "root"
proxmox_password = "gawrgare"
- Now it’s time to add the Proxmox related terraform configurations on the
talos.tffile
locals {
nodes = {
"talos-control-plane" = {
"node_name" = var.proxmox_node_name
"vm_id" = 110
"cpu" = 2
"tags" = ["kubernetes", "control-plane"]
}
"talos-worker-0" = {
"node_name" = var.proxmox_node_name
"vm_id" = 111
"cpu" = 2
"tags" = ["kubernetes", "worker"]
}
}
bootable = {
type = "iso"
file_name = "talos-v1.11.1.iso"
url = "https://factory.talos.dev/image/efb7577422715f84c716c3d30fee60858fb093841d1d539ca5db92ae99737bf8/v1.11.1/metal-amd64.iso"
}
}
resource "proxmox_virtual_environment_download_file" "talos_image" {
content_type = local.bootable.type
datastore_id = "local"
node_name = var.proxmox_node_name
file_name = local.bootable.file_name
url = local.bootable.url
}
resource "proxmox_virtual_environment_vm" "talos" {
for_each = local.nodes
tags = each.value.tags
name = each.key
node_name = each.value.node_name
vm_id = each.value.vm_id
bios = "seabios"
description = "Managed by Terraform"
started = false
template = false
agent {
enabled = true
}
cpu {
cores = each.value.cpu
type = "x86-64-v2-AES"
}
memory {
dedicated = 4096
}
disk {
datastore_id = var.proxmox_datastore_id
file_id = proxmox_virtual_environment_download_file.talos_image.id
interface = "scsi0"
iothread = true
discard = "on"
size = 100
}
initialization {
ip_config {
ipv4 {
address = "dhcp"
}
}
}
network_device {
bridge = "vmbr0"
}
}
What the codeblocks gonna do
- It creates a locals variable that adds two nodes
control-planeandworker - We will use
proxmox_virtual_download_fileto download the.isofiles and keep it in ourProxmoxstorage. You can change theURLbased on yourschematics - We will create a VM with following configurations
- 100GB of disk
- Dynamic IP Address
- 2 Cores CPU
- 4 GB of RAM
- QEMU Agent Enabled
TIP
Please refer to official terraform documentationfor the detail configurations I set
started = falsebecause sometimes the terraform state will get stuck, so we need to turn on the VM manually You can Configure Talos using terraform too with this Talos Providers but i will do it manually in this tutorial
Configure Talos
- We need to Install
talosctlto configure our cluster. Since i’m in MacOS I will be using brew for this. For other OS you can see official documentation
brew install siderolabs/tap/sidero-tools- We will need to export a variable of
CONTROL_PLANEandWORKER_IP
export CONTROL_PLANE_IP=(your IP)
export WORKER_IP=(your worker IP)- We will generate config using
talosctl gen config
talosctl gen config talos-proxmox-cluster https://$CONTROL_PLANE_IP:6443 --output-dir _out --install-image factory.talos.dev/installer/efb7577422715f84c716c3d30fee60858fb093841d1d539ca5db92ae99737bf8:v1.11.1What this command do? It will generate talos cluster config with the
- Cluster Name of:
talos-proxmox-cluster - Control Plane Address:
https://$CONTROL_PLANE_IP:6443 - Will output the result in
_outdirectory - It will generate based on the our choice of ISO
- Now we need to export the variable of
TALOSCONFIG
export TALOSCONFIG="_out"
- Now we need to apply our generated configurations to our cluster both on Control Plane and Worker
talosctl --talosconfig $TALOSCONFIG apply-config --insecure --nodes $CONTROL_PLANE_IP --file _out/controlplane.yamlApply again for our worker
talosctl --talosconfig $TALOSCONFIG apply-config --insecure --nodes $WORKER_IP --file _out/worker.yaml- Finally we can set the informations about our node endpoint and info
talosctl --talosconfig $TALOSCONFIG config endpoint $CONTROL_PLANE_IP
talosctl --talosconfig $TALOSCONFIG config node $CONTROL_PLANE_IP
talosctl --talosconfig $TALOSCONFIG config infoIf it configured correctly it will show something like this
Current context: talos-proxmox-cluster
Nodes: 192.168.1.57
Endpoints: 192.168.1.57
Roles: os:admin
Certificate expires: 11 months from now (2026-09-16)
- Finally, we can apply all of the current configurations and bootstrap the cluster using these commands
talosctl --talosconfig $TALOSCONFIG bootstrapThe OS will restart and stage will be move to BOOTING state
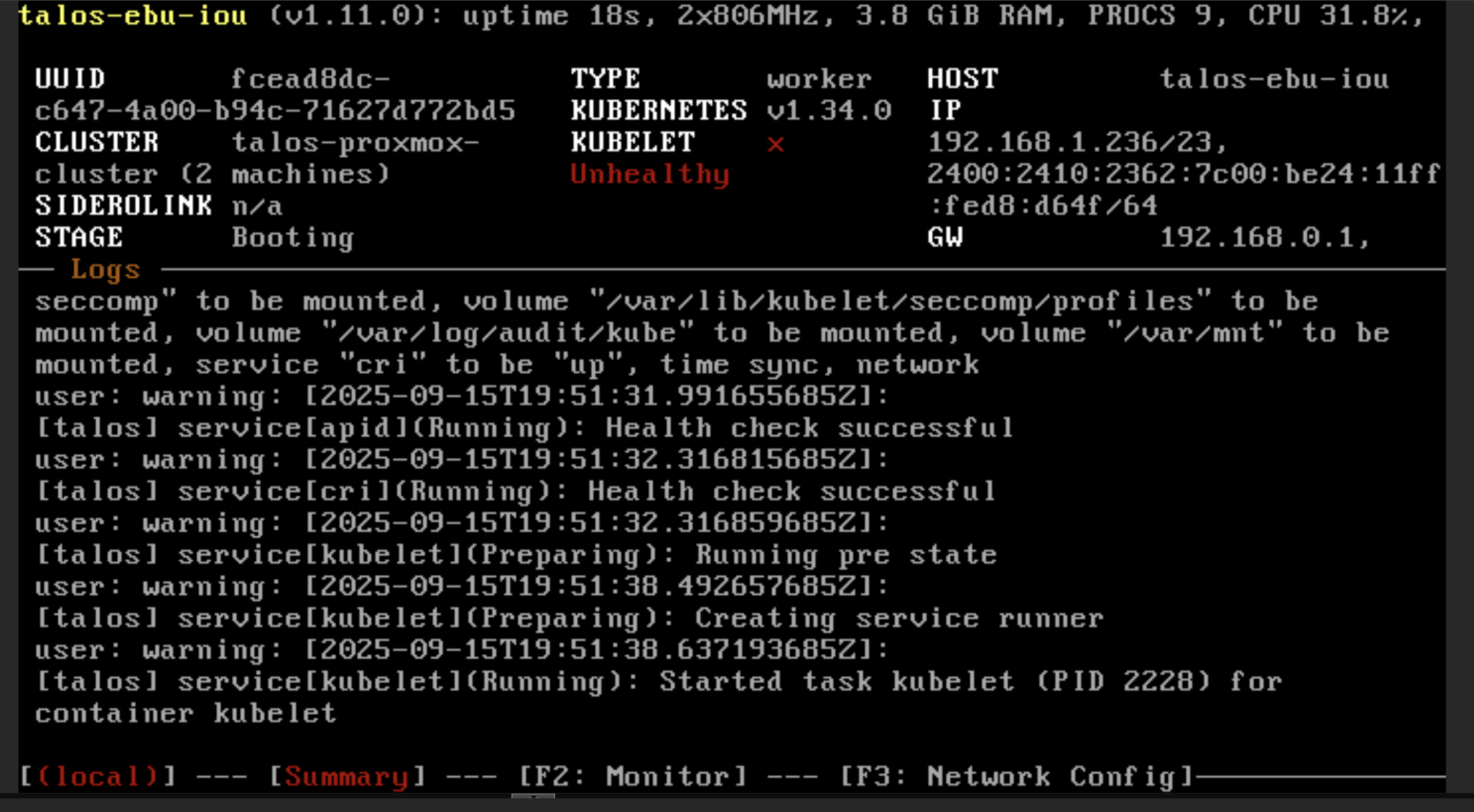
Wait until the state to be READY and KUBELET is active
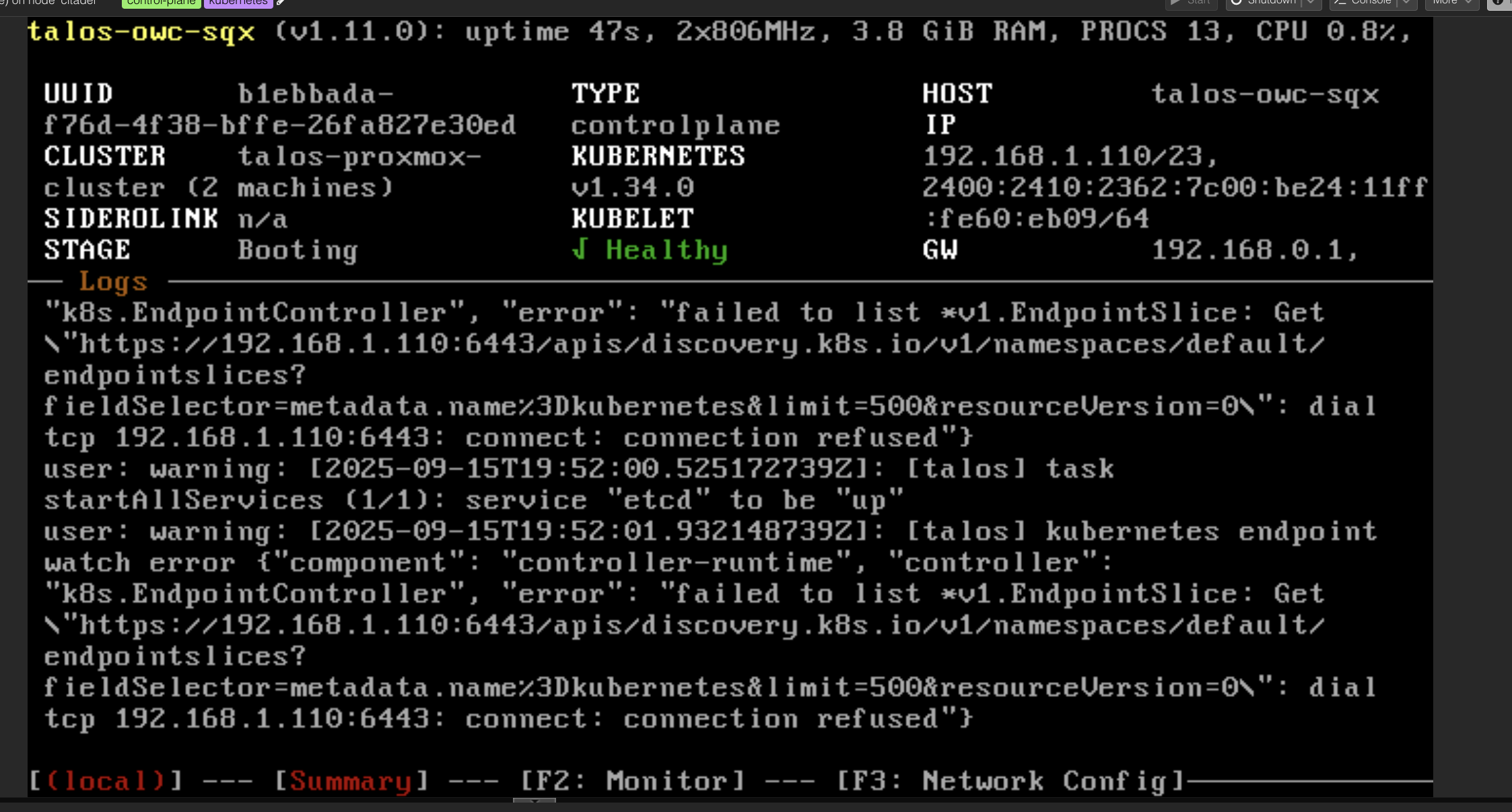
Configuring Kubernetes
After the kubelet is healthy now we can get the kubeconfig for our cluster
talosctl --talosconfig $TALOSCONFIG kubeconfigUsually, our kubectl will search the kubeconfig via KUBECONFIG env variable and will be fallback to the ~/.kube/config
The kubeconfig file will contains the configurations for our cluster, we can add it in two ways
- Add using env variable
export KUBECONFIG=(PATH_TO_CLUSTER_KUBECONFIG)
- Merge the generated
kubeconfigand~/.kube/config.
I prefer option no 2 since it taught me a lot about how does kubeconfig works under the hood.
Verify the correctness using kubectl config get-contexts. You should see the talos cluster there
Switch the context to use the our cluster configurations by using
kubectl config use-context admin@talos-proxmox-cluster
Now try to get all nodes informations by using
kubectl get nodes -o wideYou should see the service/kubernetes all the information about your clusters
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION INTERNAL-IP EXTERNAL-IP OS-IMAGE KERNEL-VERSION CONTAINER-RUNTIME
talos-dgk-fip Ready <none> 12d v1.34.0 192.168.1.133 <none> Talos (v1.11.1) 6.12.45-talos containerd://2.1.4
talos-zbn-kx5 Ready control-plane 12d v1.34.0 192.168.1.57 <none> Talos (v1.11.1) 6.12.45-talos containerd://2.1.4
Deploying Nginx pod
After the setup is completed we want to test our cluster behavior by deploying and nginx pod. Create a pod.yaml file with this content
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: nginx-pod
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx-container
image: nginx:latest
ports:
- containerPort: 80Now apply the pod by using these commands
kubectl apply -f `pod.yaml`Verify by using curl inside the localhost
kubectl exec pod/nginx-pod -- curl localhost<html>
<head>
<title>Welcome to nginx!</title>
<style>
html { color-scheme: light dark; }
body { width: 35em; margin: 0 auto;
font-family: Tahoma, Verdana, Arial, sans-serif; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Welcome to nginx!</h1>
<p>If you see this page, the nginx web server is successfully installed and
working. Further configuration is required.</p>
<p>For online documentation and support please refer to
<a href="http://nginx.org/">nginx.org</a>.<br/>
Commercial support is available at
<a href="http://nginx.com/">nginx.com</a>.</p>
<p><em>Thank you for using nginx.</em></p>
</body>
</html>
Neat! now our cluster is working properly and good! don’t forget to remove the nginx by using
kubectl delete -f `pod.yaml`FAQ
Upgrading talos linux
When you want to upgrade talos linux you can use this commands
talosctl --talosconfig talosconfig upgrade --image factory.talos.dev/metal-installer/6d1f5bd37d6a6bf937ad651c5482d93571942c19bb32dde87b6a17b5e443ec39:v1.11.1 --nodes 192.168.1.144,192.168.1.117 --preserveHow to access this outside of our homenetwork
I use tailscale for this. Tailscale is some kind of VPN that create a mesh network of all our devices. We can register our Proxmox VM as a tailscale node and we can ssh to go inside and do the kubectl operating
- If you want to manually apply in your local machine, you can make your Proxmox VM a subnet router so you can forward the network directly to your cluster
I try to install stateful set but i got an error
By default talos OS doesn’t have a Storage Class see the documentation for the details. But since we already install some of the iscsi-tools as our extentions, We can directly install it by adding longhorn.yaml
machine:
kubelet:
extraMounts:
- destination: /var/lib/longhorn
type: bind
source: /var/lib/longhorn
options:
- bind
- rshared
- rwAnd then patch our current cluster by using these commands with 192.168.1.57,192.168.1.133 being the IP of our cluster nodes
talosctl --talosconfig talosconfig patch machineconfig -p @longhorn.yaml -n 192.168.1.57,192.168.1.133Remarks
With this project i learn a lot of stuff
- Storage system in kubernetes
- How does Proxmox work
- How can we setup our own Kubernetes cluster
I hope this guide could be helpful to u and don’t hesitate to ping me if you have a questions regarding this. All of the code could be found in my citadel repository